

Ahmed and Israa 13 investigated the impact of dust on the performance of a PV system in Sharjah desert, showing significant deterioration of efficiency because of the dust accumulation. The wind-tunnel experiments 12 and in-situ observations in real environments are generally designed to realize the impact behavior of particles to evaluate the effects of dusty and sandy environments on ground-based PV panels. The previous study for the impact of dust mainly focused on the power output and efficiency change. sandy weather, desert storms, volcanic eruptions and so on) 11. industrial emissions, construction debris, highway activities and so on) or natural environment (i.e.
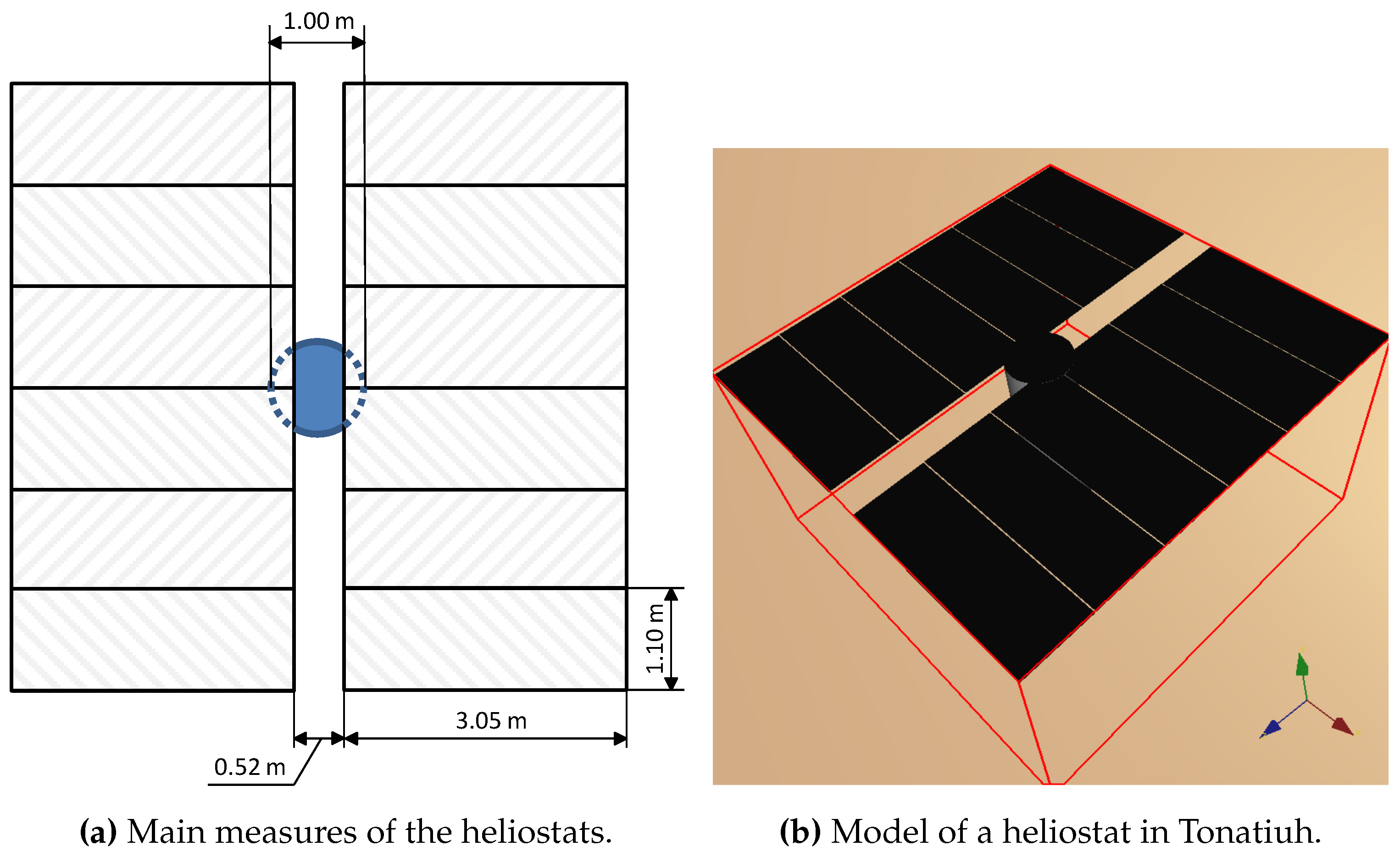
There will be inevitable impact or deposition of dust that can be induced by human activities (i.e. Dust impact loadings such as windy, sandy deposition, and debris impact, which can significantly reduce the efficiency of PV cells in an intrinsically coupled pattern and even lead to ultimately failure 8, 9, 10, posing great challenges in their application in-field use. Dust is an unavoidable factor that affects solar PV module performance and is considered as one of the major factors that contribute to the formation of hot spots 8, 9 in a PV module. Actually, not only will the transport of the PV modules but also their storage and unsuitable handling during installation lead to performance reduction or potential faults 7. PV modules are often installed in the harsh outdoor environment and thus tend to suffer several kinds of faults, causing unexpected safety issues, power losses, and even fire hazards 4, 5, 6. Among all possible candidates, the monolithic triple-junction cells (GaInP/GaInAs/Ge) are extensively used because of their high resistance to thermal degradation 3. Thin-film multi-junction photovoltaic (PV) cells made from the compounds of III–V materials have been widely adopted due to their high light-electricity conversion efficiency and low areal mass density 1, 2. Moreover, three damage modes, including damaged conducting grid lines, fractured PV cell surfaces, and the bending effects after impact are observed, and the corresponding strength of each mode is quantified by different mechanical theories. A damage-induced conversion efficiency degradation (DCED) model is developed and validated by experiments, providing an effective method in predicting the performance degradation of PV cells under various dust impact conditions. It drops from 26.7 to 3.9% with increasing the impact velocity from 40 to 185 m/s and the particles’ number densities from 35 to 150/mm 2, showing a reduction up to 85.7% when being compared with the intact ones with the light-electricity conversion efficiency of 27.2%. The results show that the light-electricity conversion efficiency of the PV cells decreases with increasing the impact velocity and the particles’ number density. In this paper, the performance degradation and the damage behavior of PV cells subjected to massive dust impact are investigated using laser-shock driven particle impact experiments and mechanical modeling.

It has been a key issue for photovoltaic (PV) cells to survive under mechanical impacts by tiny dust.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
